AI Navigation Assistant
Agentic AI app design and developments to simplify, accelerate, and improve accuracy in manual data collection
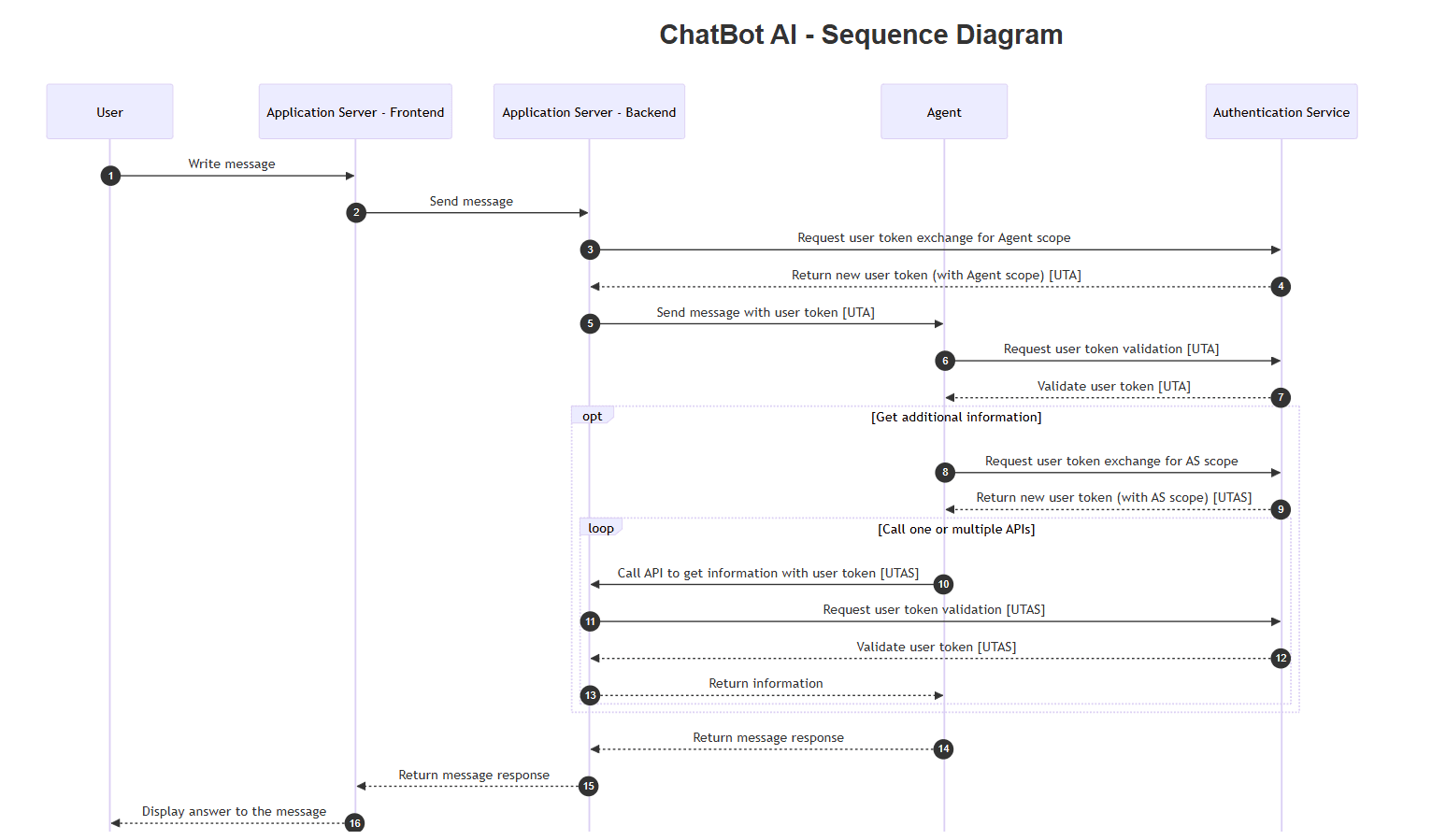
Creating a new agentic AI-enabled user experience in navigating the enterprise software platform with the new AI Navigation Assistant. Through conversational AI, the Navigation Assistant transforms how users interact with Wolters Kluwer Enablon's environmental, health, and safety (EHS) platform.
Role: UX Designer / Research / Vibe coding prototyper
Timeline: September, 2025 - present
Team: Design team, Product team, and Data Lab
Conversational AI workflow
Users' action with AI
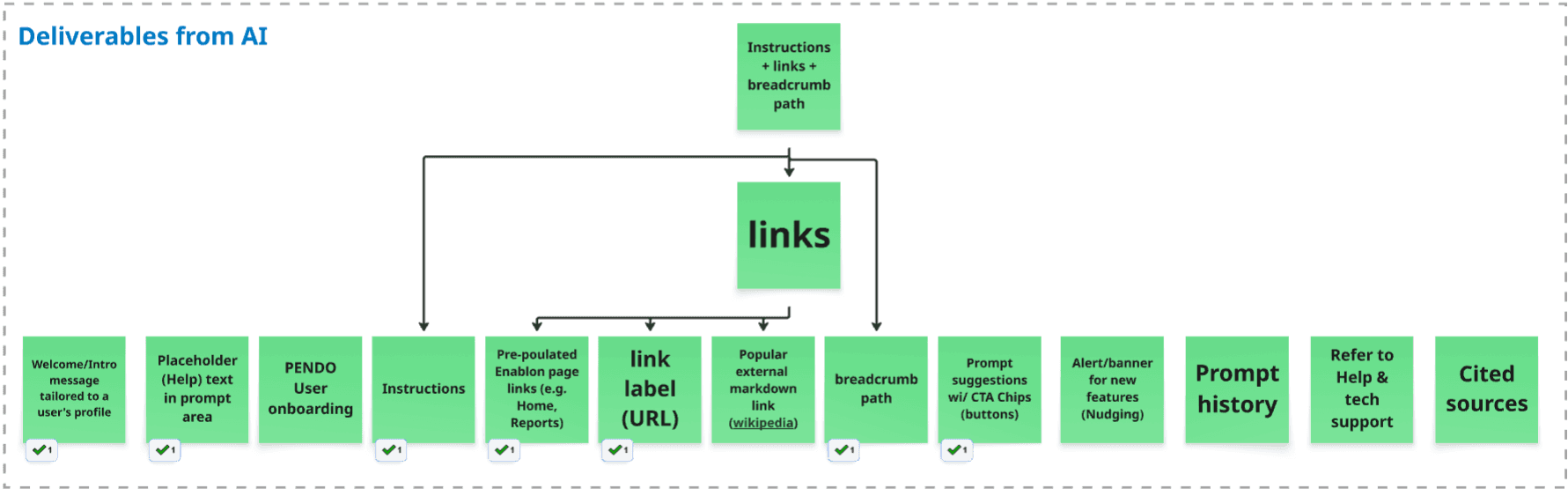
Planning for the deliverables from AI
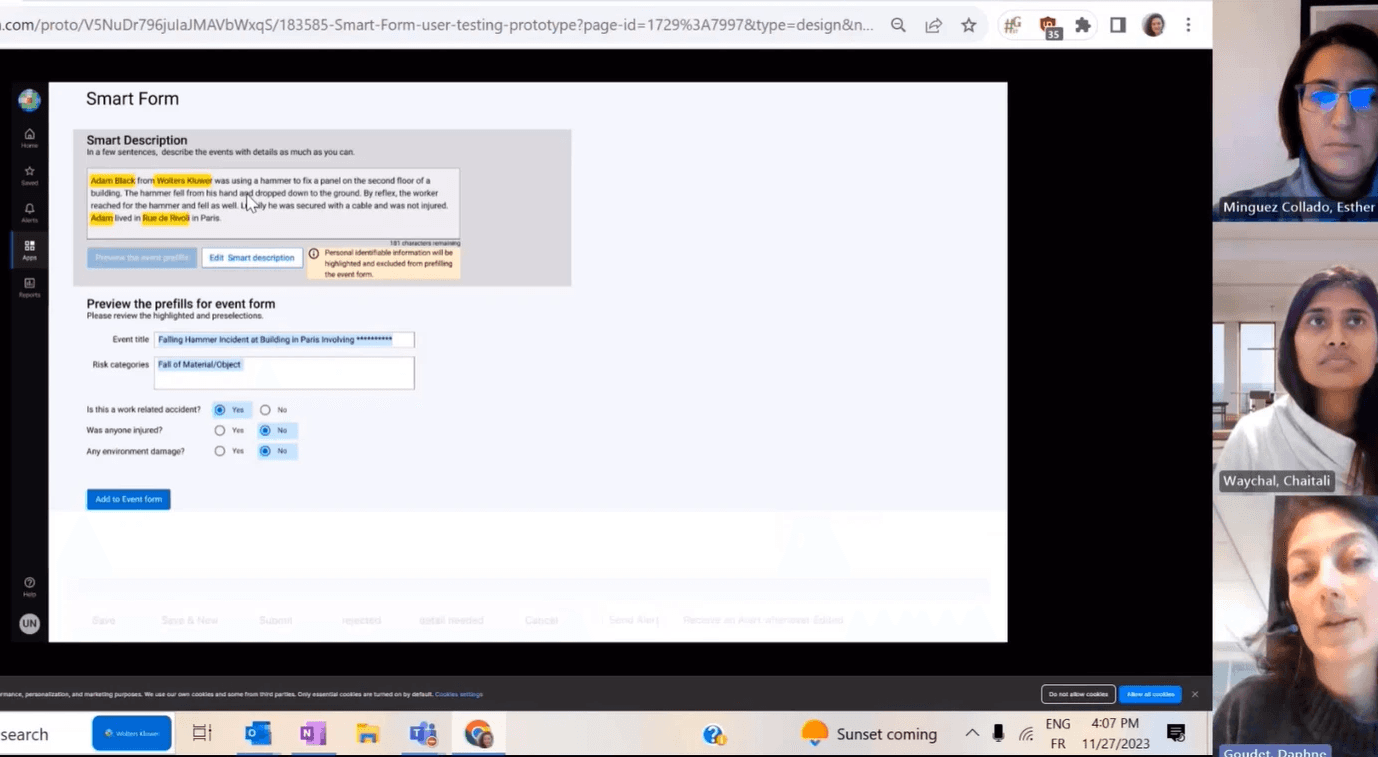
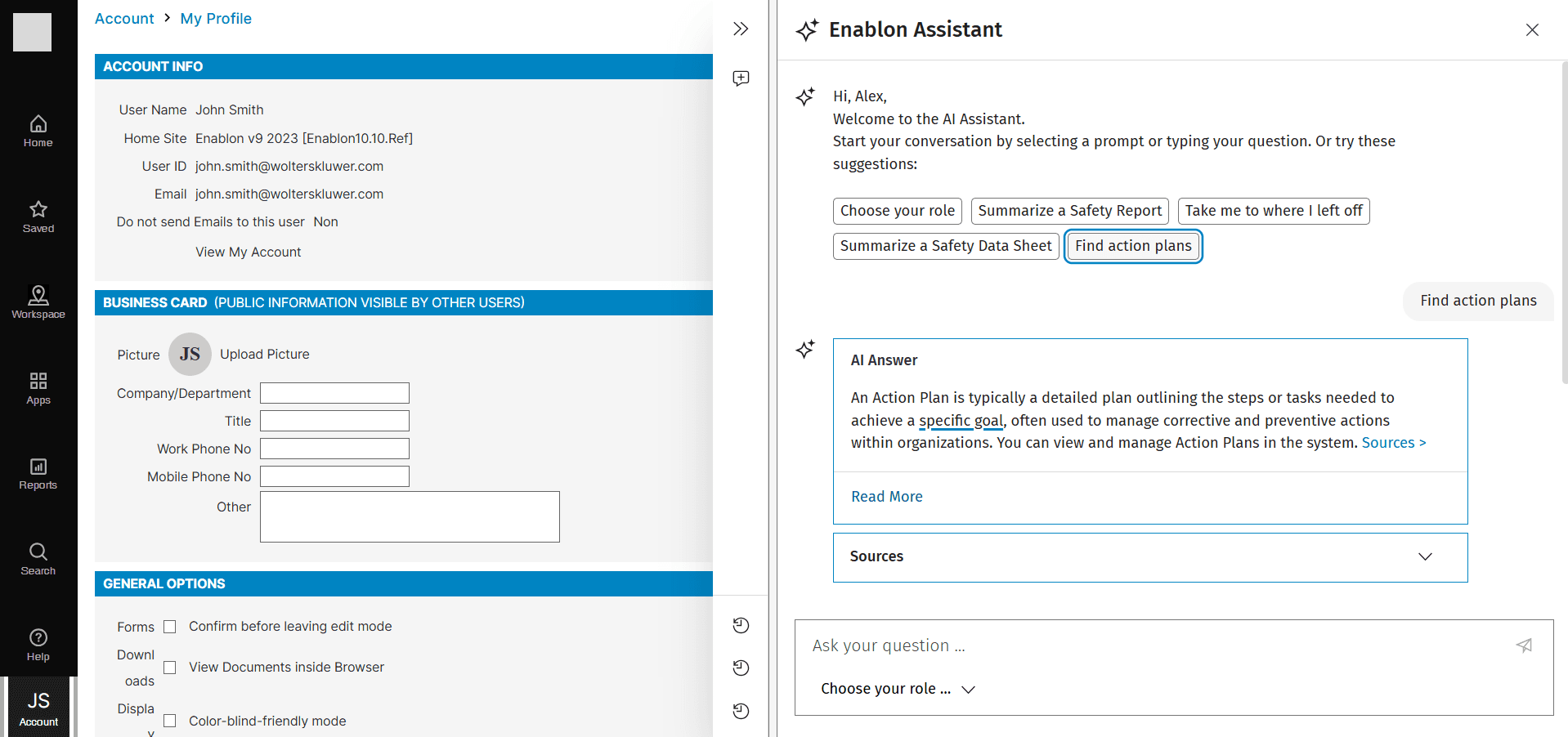
Demo on prompting and AI responses
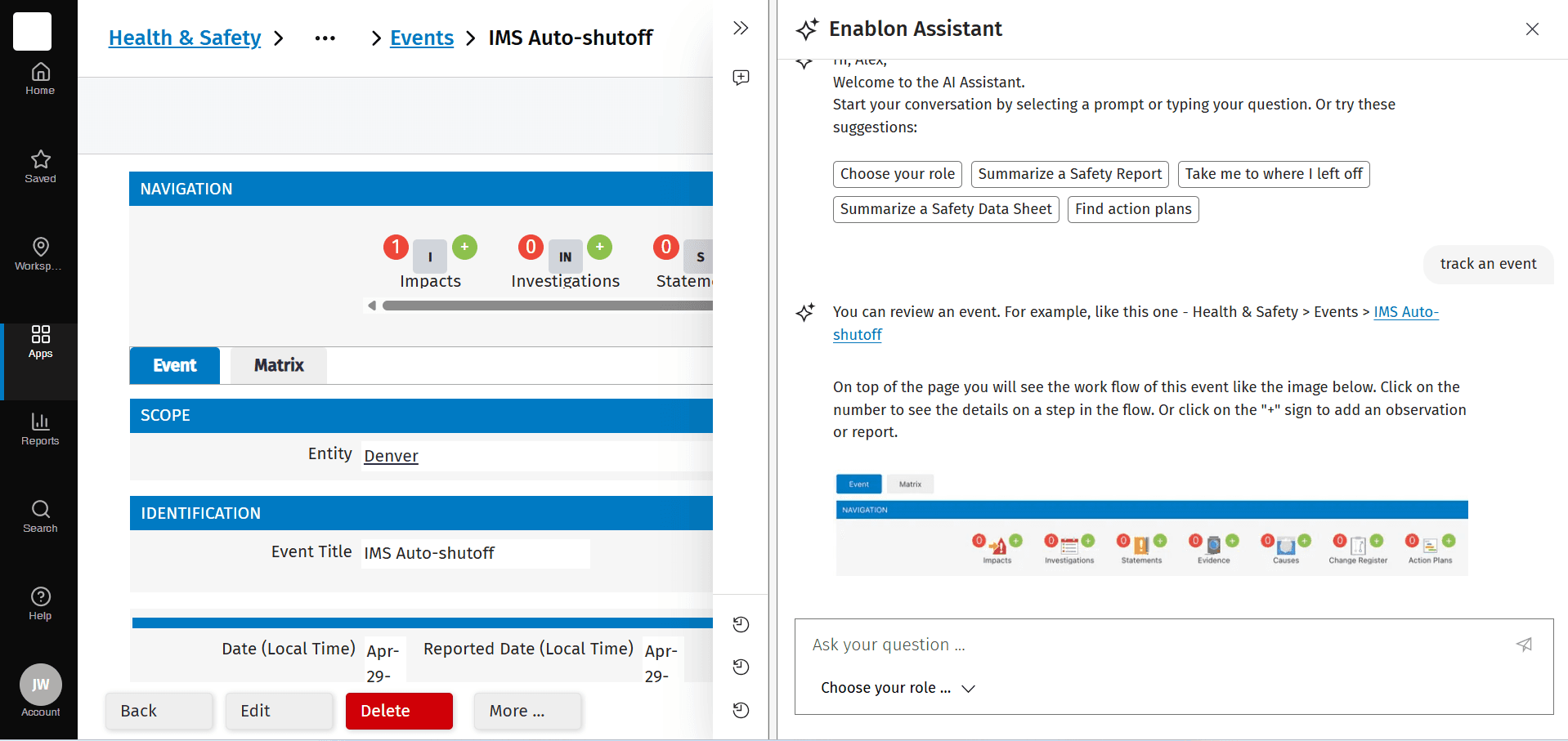
User onboarding by AI
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) for hybrid search
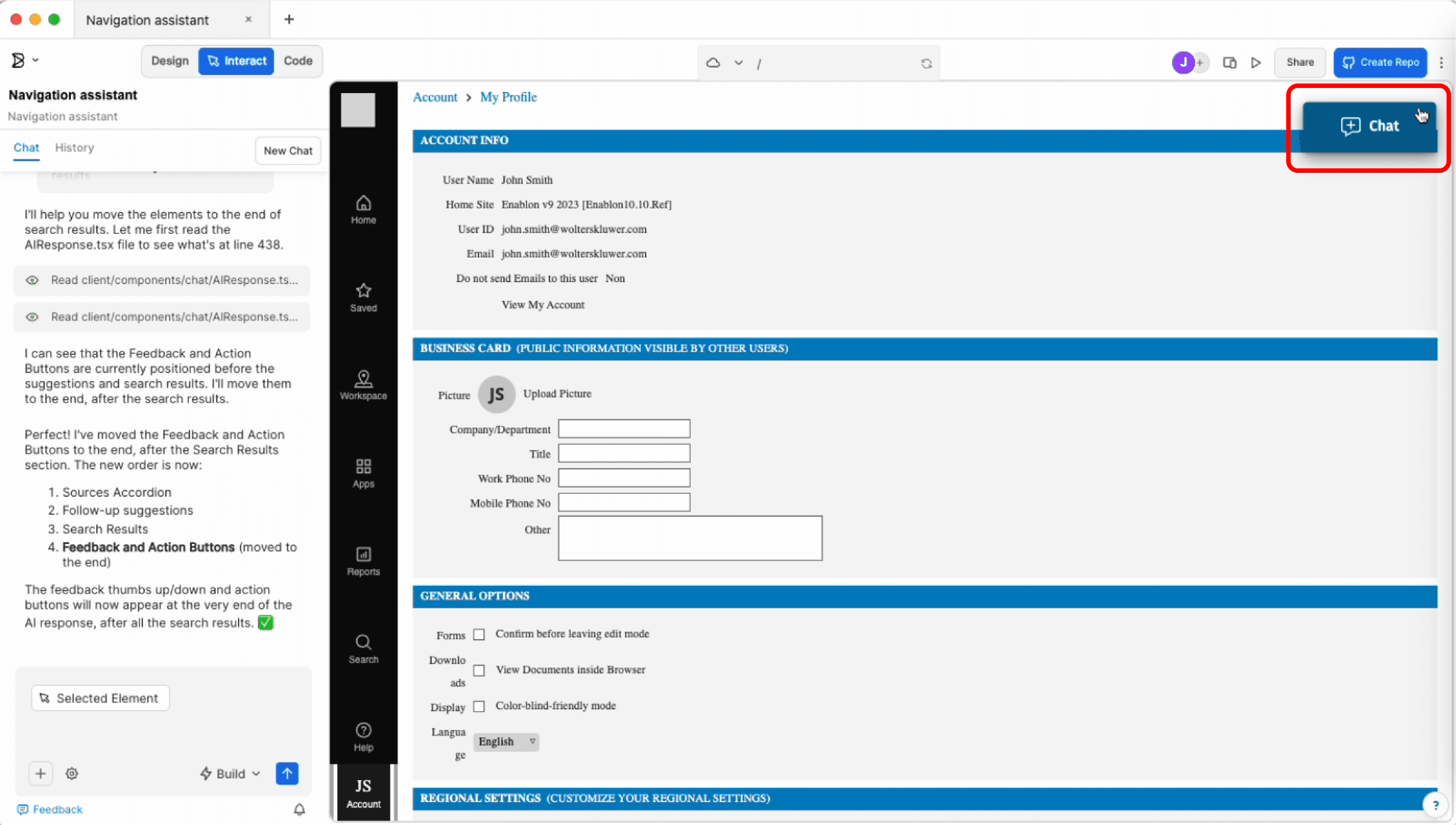
Vibe coding for design and prototyping
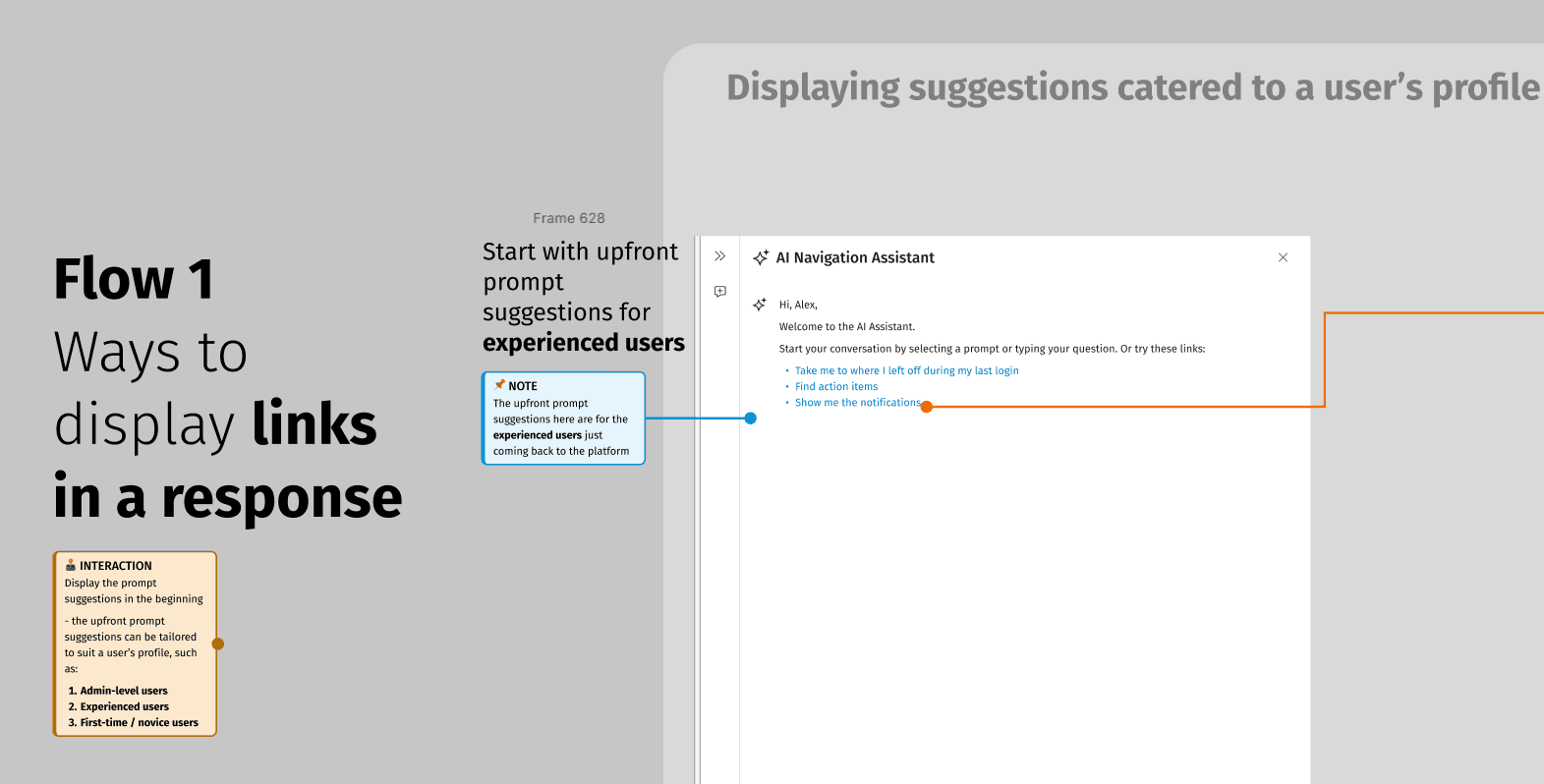
Exploring ways to display links in AI response
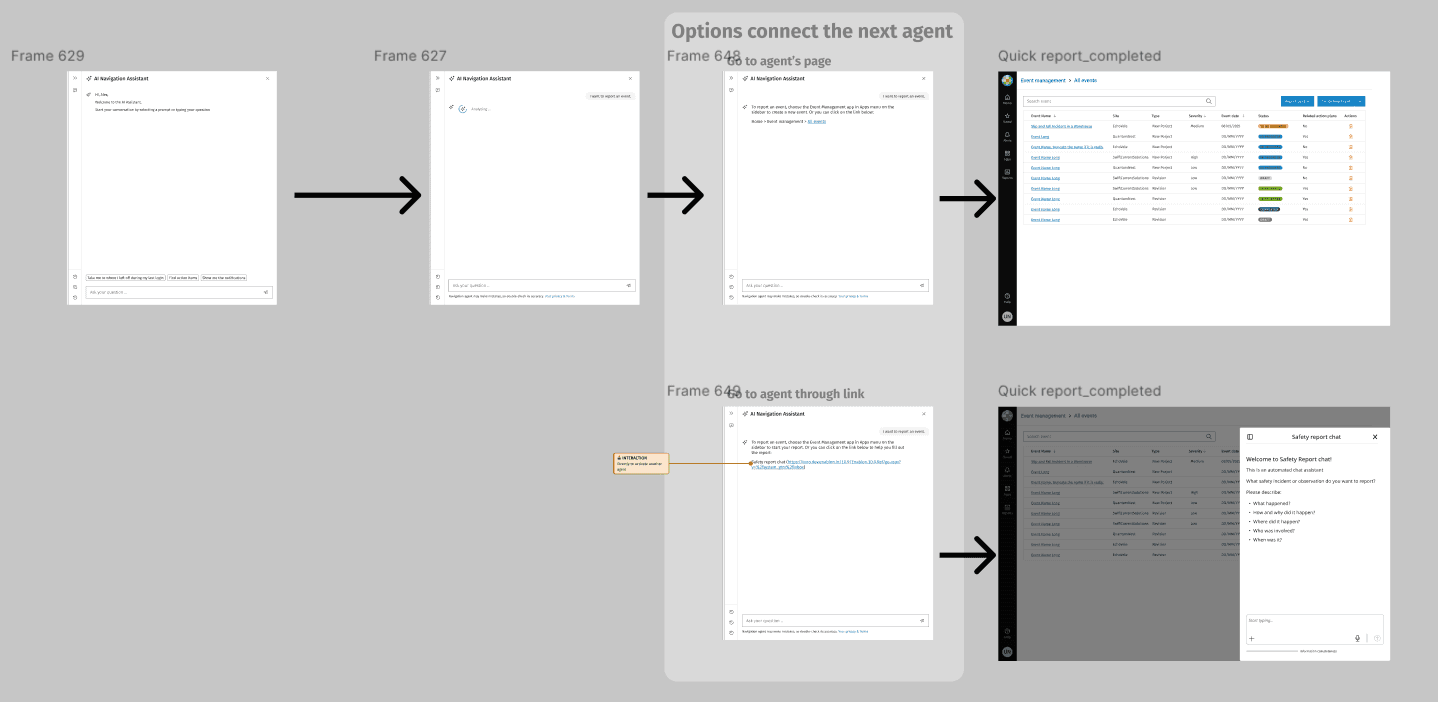
User flow for orchestrator to connect with another agent
Vibe coding and prototyping on Builder.io
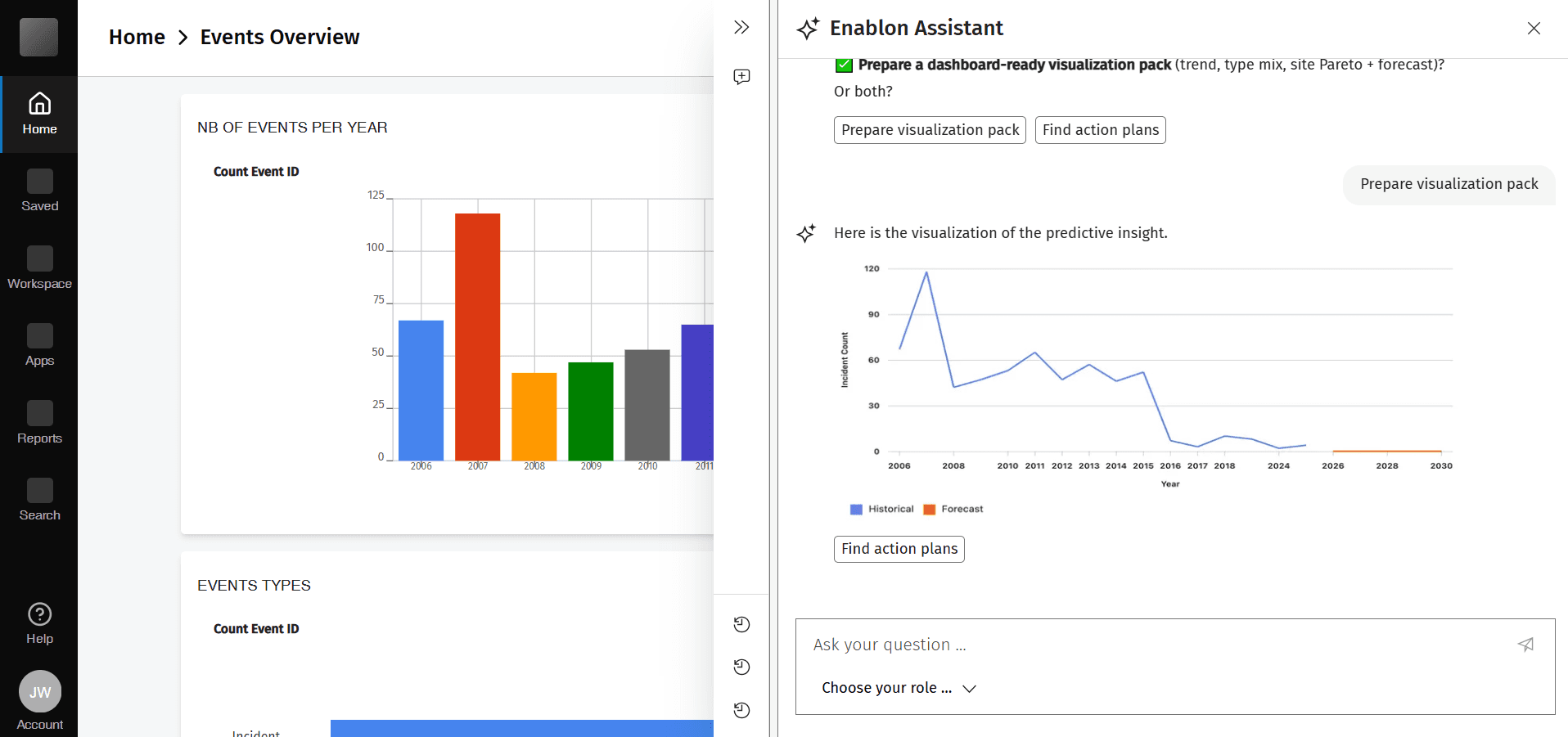
AI response pattern design for predictive analytics
Challenges
User Pain Points - the identified critical navigation issues affecting our users’ daily platform usage:
Outdated interface: Users described the current platform as "clunky" with a design aesthetic resembling early 2000s software
Complex navigation: Difficulty finding and accessing key functions through traditional menu structures
Cognitive load: Users struggled to remember where specific features were located across the extensive platform
This created tension between two key user groups: EHS managers in control rooms needed timely, accurate reporting, while field operators needed quick, mobile-friendly access that wouldn't disrupt their workflow.
Opportunity
Rather than another incremental redesign, we saw an opportunity to leverage emerging AI capabilities to fundamentally transform user interaction.
Key Insight: What if users could simply tell the system what they want to do, rather than hunting through menus?
Design Vision
From Static to Conversational
I envisioned transforming the traditional point-and-click interface into an intelligent conversational experience where users interact naturally with the platform:
User asks:
"I want to report an incident"
"How to log a near miss"
"Can I see the list of action plans"
"Where are the audits"
System responds: Display the direct navigation link to the appropriate destination through contextual understanding.
Design Research & Strategy
Understanding AI UX in 2026
To design effectively for this new paradigm, I researched:
Current state of AI interfaces: How users interact with conversational AI and their expectations.
AI capabilities and limitations: Understanding what happens under the hood to design realistic experiences
Key Design Considerations
Detecting User Intent
Developing techniques to help users articulate their needs clearly.
Building Trust
Fostering user confidence in AI-generated responses by setting guardrails against inaccuracy and hallucination.
Dynamic vs. Static Interaction
Designing flexible, proactive experiences that adapt to user needs rather than rigid, deterministic flows.
Individual Personalization
Tailoring AI responses to align with user preferences and frequently-accessed features.
Solution Architecture
The Navigation Assistant
I designed a natural language navigation system that:
Interprets user intent from conversational queries ("go to," "create," "search")
Translates requests into specific URLs for the Enablon web application
Provides hierarchical paths, such as breadcrumbs, supplemented by target URL
Accommodates licensing restrictions (users can only access features they're authorized for)
Maintains context for follow-up interactions
Response Style: Concise and professional, providing breadcrumb paths followed by target URLs.
Design Patterns & Innovations
Novel Interaction Patterns
Proactive accommodation: System anticipates user needs based on context and history. Examples include prompt suggestions.
Information Architecture
Designed hierarchical navigation responses that provide:
Clear breadcrumb paths showing location context
Multiple options when queries are ambiguous
Consistent tone and voice across different interaction types
Technical Collaboration
Working Within Platform Capabilities
I collaborated closely with technical teams to design within current capabilities:
FAB (WK GenAI hub): Leveraging available LLM models and FAB Expy library of AI interaction patterns and element
Data Lab team: Ensuring data access and processing requirements were feasible
Front-End Core team: Designing interaction patterns and elements that could be implemented
AI Services Platform: Integrating new AI agents with the application platform
Impact & Next Steps
Transforming Enterprise Software Interaction
This project represents a fundamental shift in how users interact with complex enterprise platforms—from mechanical menu navigation to natural and dynamic conversation. Upcoming developments are:
Conducting user testing, using metrics, such as user satisfaction, time savings
Establish design framework for future AI services (augmented search or a hybrid of search and AI answer)
Create scalable design patterns supporting multiple AI use cases
Experiment with new AI design tools, such as Builder.io, to accelerate design exploration
Future Vision
The intention detection layer provides foundation for expanding conversational AI across the platform. It will work as an orchestrator to welcome and onboard users first, then detect users’ intentions and direct users to agents like Navigation Assistant, Report Writer, or Safety Adviser agent.
Reflections
What I Learned
New interaction pattern: transforming static and deterministic interaction into engaging, dynamic, flexible, proactive experiences that accommodate user needs rather than rigid, deterministic flows.
In conversational AI, designers cannot fully predict how an AI agent will respond to every user prompt. I took a holistic research approach: studying existing AI use cases and analyzing pioneer AI models to anticipate likely response patterns. This research allowed me to envision possible scenarios and design appropriate response formats, ensuring the AI agent would deliver consistent, helpful interactions even with unpredictable user inputs.
Design Challenges
What response format should be used according to AI’s confidence level?
When users ask an out-of-scope question or request - Creating graceful responses
Handling ambiguous queries: The interface needed to elegantly surface options without overwhelming users.
Managing user expectations: users mostly have high expectations for natural conversation, but our V1 focused specifically on navigation. We had to balance user assumptions about what the system could do with realistic scope constraints.
Designing for AI limitations: Unlike deterministic UI, AI responses can vary and occasionally fail. I designed feedback patterns, error states, and fallback mechanisms that maintained user confidence even when the system couldn't provide perfect answers.